 Sexuality is a complex characteristic that involves the physical, psychological, interpersonal, and behavioral aspects of a person. Recognizing that "normal" sexual functioning covers a wide range is important. Ultimately, sexuality is defined by each patient and his/her partner according to sex, age, personal attitudes, and religious and cultural values.
Many types of cancer and cancer therapies can cause sexual dysfunction. Research shows that approximately 50% of women who have been treated for breast and gynecologic cancers experience long-term sexual dysfunction. Nearly 70% of men who have been treated for prostate cancer experience long-term sexual dysfunction.
An individual's sexual response can be affected in many ways. The causes of sexual dysfunction are often both physical and psychological. The most common sexual problems for people who have cancer are loss of desire for sexual activity in both men and women, problems achieving and maintaining an erection in men, and pain with intercourse in women. Men may also experience inability to ejaculate, ejaculation going backward into the bladder, or the inability to reach orgasm. Women may experience a change in genital sensations due to pain, loss of sensation and numbness, or decreased ability to reach orgasm. Most often, both men and women are still able to reach orgasm, however, it may be delayed due to medications and/or anxiety.
Unlike many other physical side effects of cancer treatment, sexual problems may not resolve within the first year or two of disease-free survival and can interfere with the return to a normal life. Patients recovering from cancer should discuss their concerns about sexual problems with a health care professional.
Factors Affecting Sexual Function in People With Cancer
Both physical and psychological factors contribute to the development of sexual dysfunction. Physical factors include loss of function due to the effects of cancer therapies, fatigue, and pain. Surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy may have a direct physical impact on sexual function. Other factors that may contribute to sexual dysfunction include pain medications, depression, feelings of guilt from misbeliefs about the origin of the cancer, changes in body image after surgery, and stresses due to personal relationships. Getting older is often associated with a decrease in sexual desire and performance, however, sex may be important to the older person's quality of life and the loss of sexual function can be distressing.
Surgery-Related Factors
Surgery can directly affect sexual function. Factors that help predict a patient's sexual function after surgery include age, sexual and bladder function before surgery, tumor location and size, and how much tissue was removed during surgery. Surgeries that affect sexual function include breast cancer, colorectal cancer, prostate cancer, and other pelvic tumors.
Breast Cancer
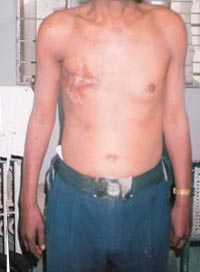
Sexual function after breast cancer surgery has been the subject of much research. Surgery to save or reconstruct the breast appears to have little effect on sexual function compared with surgery to remove the whole breast. Women who have surgery to save the breast are more likely to continue to enjoy breast caressing, but there is no difference in areas such as how often women have sex, the ease of reaching orgasm, or overall sexual satisfaction.
Colorectal Cancer
Sexual and bladder dysfunctions are common complications of surgery for rectal cancer. The main cause of problems with erection, ejaculation, and orgasm is injury to nerves in the pelvic cavity. Nerves can be damaged when their blood supply is disrupted or when the nerves are cut.
Prostate Cancer
Newer nerve-sparing techniques for radical prostatectomy are being debated as a more successful approach for preserving erectile function than radiation therapy for prostate cancer. Long-term follow-up is needed to compare the effects of surgery with the effects of radiation therapy. Recovery of erectile function usually occurs within a year after having a radical prostatectomy. The effects of radiation therapy on erectile function are very slow and gradual occurring for two or three years after treatment. The cause of loss of erectile function differs between surgery and radiation therapy. Radical prostatectomy damages nerves that make blood vessels open wider to allow more blood into the penis. Eventually the tissue does not get enough oxygen, cells die, and scar tissue forms that interferes with erectile function. Radiation therapy appears to damage the arteries that bring blood to the penis.
Other Pelvic Tumors
Men who have surgery to remove the bladder, colon, and/or rectum may improve recovery of erectile function if nerve-sparing surgical techniques are used. The sexual side effects of radiation therapy for pelvic tumors are similar to those after prostate cancer treatment. Women who have surgery to remove the uterus, ovaries, bladder, or other organs in the abdomen or pelvis may experience pain and loss of sexual function depending on the amount of tissue/organ removed. With counseling and other medical treatments, these patients may regain normal sensation in the vagina and genital areas and be able to have pain-free intercourse and reach orgasm.
Chemotherapy-Related Factors
Chemotherapy is associated with a loss of desire and decreased frequency of intercourse for both men and women. The common side effects of chemotherapy such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, mucositis, weight loss or gain, and loss of hair can affect an individual's sexual self-image and make him or her feel unattractive.
For women, chemotherapy may cause vaginal dryness, pain with intercourse, and decreased ability to reach orgasm. In older women, chemotherapy may increase the risk of ovarian cancer. Chemotherapy may also cause a sudden loss of estrogen production from the ovaries. The loss of estrogen can cause shrinking, thinning, and loss of elasticity of the vagina, vaginal dryness, hot flashes, urinary tract infections, mood swings, fatigue, and irritability. Young women who have breast cancer and have had surgeries such as removal of one or both ovaries, may experience symptoms related to loss of estrogen. These women experience high rates of sexual problems since there is a concern that estrogen replacement therapy, which may decrease these symptoms, could cause the breast cancer to return. For women with other types of cancer, however, estrogen replacement therapy can usually resolve many sexual problems. Also, women who have graft-versus-host disease (a reaction of donated bone marrow or peripheral stem cells against a person's tissue) following bone marrow transplantation may develop scar tissue and narrowing of the vagina that can interfere with intercourse.
For men, sexual problems such as loss of desire and erectile dysfunction are more common after a bone marrow transplant because of graft-versus-host disease or nerve damage. Occasionally chemotherapy may interfere with testosterone production in the testicles. Testosterone replacement may be necessary to regain sexual function.
Radiation Therapy-Related Factors
Like chemotherapy, radiation therapy can cause side effects such as fatigue, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, and other symptoms that can decrease feelings of sexuality. In women, radiation therapy to the pelvis can cause changes in the lining of the vagina. These changes eventually cause a narrowing of the vagina and formation of scar tissue that results in pain with intercourse, infertility and other long term sexual problems. Women should discuss concerns about these side effects with their doctor and ask about the use of a vaginal dilator.
For men, radiation therapy can cause problems with getting and keeping an erection. The exact cause of sexual problems after radiation therapy is unknown. Possible causes are nerve injury, a blockage of blood supply to the penis, or decreased levels of testosterone. Sexual changes occur very slowly over a period of six months to one year after radiation therapy. Men who had problems with erectile dysfunction before getting cancer have a greater risk of developing sexual problems after cancer diagnosis and treatment. Other risk factors that can contribute to a greater risk of sexual problems in men are cigarette smoking, history of heart disease, high blood pressure, and diabetes.
Hormone Therapy-Related Factors
Hormone therapy for prostate cancer can decrease normal hormone levels and cause a decrease in sexual desire, erectile dysfunction, and problems reaching orgasm. Younger men do not always experience the same degree of sexual dysfunction. Some treatment centers are experimenting with delayed or intermittent hormone therapy to prevent sexual problems. It is not yet known if these modified treatments affect the long-term survival of younger men.
The effects of tamoxifen on the sexuality and mood of women who have breast cancer are not clearly understood.
Psychological Factors
Patients recovering from cancer often have anxiety or guilt that previous sexual activities may have caused their cancer. Some patients believe that sexual activity may cause the cancer to return or pass the cancer to their partner. Discussing their feelings and concerns with a health care professional is important for patients. Misbeliefs can be corrected and patients can be reassured that cancer is not passed on through sexual contact.
Loss of sexual desire and a decrease in sexual pleasure are common symptoms of depression. Depression is more common in patients with cancer than in the general healthy population. It is important that patients discuss their feelings with their doctor. Getting treatment for depression may be helpful in relieving sexual problems.
Cancer treatments may cause physical changes that affect how an individual sees his or her physical appearance. This view can make a man or woman feel sexually unattractive. It is important that patients discuss these feelings and concerns with a health care professional. Patients can learn how to deal effectively with these problems.
The stress of being diagnosed with cancer and undergoing treatment for cancer can make existing problems in relationships even worse. The sexual relationship can also be affected. Patients who do not have a committed relationship may stop dating because they fear being rejected by a potential new partner who learns about their history of cancer. One of the most important factors in adjusting after cancer treatment is the patient's feeling about his or her sexuality before being diagnosed with cancer. If patients had positive feelings about sexuality, they may be more likely to resume sexual activity after treatment for cancer.
Assessment of Sexual Function in People with Cancer
Sexual function is an important factor that adds to quality of life. Patients should discuss their problems and concerns about sexual function with their doctor. Some doctors may not have the appropriate training to discuss sexual problems. Patients should ask for other information resources or for a referral to a health care professional who is comfortable with discussing sexuality issues.
General Factors Affecting Sexual Functioning
When a possible sexual problem is identified, the health care professional will do a detailed interview either with the patient alone or with the patient and his or her partner. The patient may be asked any of the following questions about his or her current and past sexual functioning:
Sexuality is a complex characteristic that involves the physical, psychological, interpersonal, and behavioral aspects of a person. Recognizing that "normal" sexual functioning covers a wide range is important. Ultimately, sexuality is defined by each patient and his/her partner according to sex, age, personal attitudes, and religious and cultural values.
Many types of cancer and cancer therapies can cause sexual dysfunction. Research shows that approximately 50% of women who have been treated for breast and gynecologic cancers experience long-term sexual dysfunction. Nearly 70% of men who have been treated for prostate cancer experience long-term sexual dysfunction.
An individual's sexual response can be affected in many ways. The causes of sexual dysfunction are often both physical and psychological. The most common sexual problems for people who have cancer are loss of desire for sexual activity in both men and women, problems achieving and maintaining an erection in men, and pain with intercourse in women. Men may also experience inability to ejaculate, ejaculation going backward into the bladder, or the inability to reach orgasm. Women may experience a change in genital sensations due to pain, loss of sensation and numbness, or decreased ability to reach orgasm. Most often, both men and women are still able to reach orgasm, however, it may be delayed due to medications and/or anxiety.
Unlike many other physical side effects of cancer treatment, sexual problems may not resolve within the first year or two of disease-free survival and can interfere with the return to a normal life. Patients recovering from cancer should discuss their concerns about sexual problems with a health care professional.
Factors Affecting Sexual Function in People With Cancer
Both physical and psychological factors contribute to the development of sexual dysfunction. Physical factors include loss of function due to the effects of cancer therapies, fatigue, and pain. Surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy may have a direct physical impact on sexual function. Other factors that may contribute to sexual dysfunction include pain medications, depression, feelings of guilt from misbeliefs about the origin of the cancer, changes in body image after surgery, and stresses due to personal relationships. Getting older is often associated with a decrease in sexual desire and performance, however, sex may be important to the older person's quality of life and the loss of sexual function can be distressing.
Surgery-Related Factors
Surgery can directly affect sexual function. Factors that help predict a patient's sexual function after surgery include age, sexual and bladder function before surgery, tumor location and size, and how much tissue was removed during surgery. Surgeries that affect sexual function include breast cancer, colorectal cancer, prostate cancer, and other pelvic tumors.
Breast Cancer
Sexual function after breast cancer surgery has been the subject of much research. Surgery to save or reconstruct the breast appears to have little effect on sexual function compared with surgery to remove the whole breast. Women who have surgery to save the breast are more likely to continue to enjoy breast caressing, but there is no difference in areas such as how often women have sex, the ease of reaching orgasm, or overall sexual satisfaction.
Colorectal Cancer
Sexual and bladder dysfunctions are common complications of surgery for rectal cancer. The main cause of problems with erection, ejaculation, and orgasm is injury to nerves in the pelvic cavity. Nerves can be damaged when their blood supply is disrupted or when the nerves are cut.
Prostate Cancer
Newer nerve-sparing techniques for radical prostatectomy are being debated as a more successful approach for preserving erectile function than radiation therapy for prostate cancer. Long-term follow-up is needed to compare the effects of surgery with the effects of radiation therapy. Recovery of erectile function usually occurs within a year after having a radical prostatectomy. The effects of radiation therapy on erectile function are very slow and gradual occurring for two or three years after treatment. The cause of loss of erectile function differs between surgery and radiation therapy. Radical prostatectomy damages nerves that make blood vessels open wider to allow more blood into the penis. Eventually the tissue does not get enough oxygen, cells die, and scar tissue forms that interferes with erectile function. Radiation therapy appears to damage the arteries that bring blood to the penis.
Other Pelvic Tumors
Men who have surgery to remove the bladder, colon, and/or rectum may improve recovery of erectile function if nerve-sparing surgical techniques are used. The sexual side effects of radiation therapy for pelvic tumors are similar to those after prostate cancer treatment. Women who have surgery to remove the uterus, ovaries, bladder, or other organs in the abdomen or pelvis may experience pain and loss of sexual function depending on the amount of tissue/organ removed. With counseling and other medical treatments, these patients may regain normal sensation in the vagina and genital areas and be able to have pain-free intercourse and reach orgasm.
Chemotherapy-Related Factors
Chemotherapy is associated with a loss of desire and decreased frequency of intercourse for both men and women. The common side effects of chemotherapy such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, mucositis, weight loss or gain, and loss of hair can affect an individual's sexual self-image and make him or her feel unattractive.
For women, chemotherapy may cause vaginal dryness, pain with intercourse, and decreased ability to reach orgasm. In older women, chemotherapy may increase the risk of ovarian cancer. Chemotherapy may also cause a sudden loss of estrogen production from the ovaries. The loss of estrogen can cause shrinking, thinning, and loss of elasticity of the vagina, vaginal dryness, hot flashes, urinary tract infections, mood swings, fatigue, and irritability. Young women who have breast cancer and have had surgeries such as removal of one or both ovaries, may experience symptoms related to loss of estrogen. These women experience high rates of sexual problems since there is a concern that estrogen replacement therapy, which may decrease these symptoms, could cause the breast cancer to return. For women with other types of cancer, however, estrogen replacement therapy can usually resolve many sexual problems. Also, women who have graft-versus-host disease (a reaction of donated bone marrow or peripheral stem cells against a person's tissue) following bone marrow transplantation may develop scar tissue and narrowing of the vagina that can interfere with intercourse.
For men, sexual problems such as loss of desire and erectile dysfunction are more common after a bone marrow transplant because of graft-versus-host disease or nerve damage. Occasionally chemotherapy may interfere with testosterone production in the testicles. Testosterone replacement may be necessary to regain sexual function.
Radiation Therapy-Related Factors
Like chemotherapy, radiation therapy can cause side effects such as fatigue, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, and other symptoms that can decrease feelings of sexuality. In women, radiation therapy to the pelvis can cause changes in the lining of the vagina. These changes eventually cause a narrowing of the vagina and formation of scar tissue that results in pain with intercourse, infertility and other long term sexual problems. Women should discuss concerns about these side effects with their doctor and ask about the use of a vaginal dilator.
For men, radiation therapy can cause problems with getting and keeping an erection. The exact cause of sexual problems after radiation therapy is unknown. Possible causes are nerve injury, a blockage of blood supply to the penis, or decreased levels of testosterone. Sexual changes occur very slowly over a period of six months to one year after radiation therapy. Men who had problems with erectile dysfunction before getting cancer have a greater risk of developing sexual problems after cancer diagnosis and treatment. Other risk factors that can contribute to a greater risk of sexual problems in men are cigarette smoking, history of heart disease, high blood pressure, and diabetes.
Hormone Therapy-Related Factors
Hormone therapy for prostate cancer can decrease normal hormone levels and cause a decrease in sexual desire, erectile dysfunction, and problems reaching orgasm. Younger men do not always experience the same degree of sexual dysfunction. Some treatment centers are experimenting with delayed or intermittent hormone therapy to prevent sexual problems. It is not yet known if these modified treatments affect the long-term survival of younger men.
The effects of tamoxifen on the sexuality and mood of women who have breast cancer are not clearly understood.
Psychological Factors
Patients recovering from cancer often have anxiety or guilt that previous sexual activities may have caused their cancer. Some patients believe that sexual activity may cause the cancer to return or pass the cancer to their partner. Discussing their feelings and concerns with a health care professional is important for patients. Misbeliefs can be corrected and patients can be reassured that cancer is not passed on through sexual contact.
Loss of sexual desire and a decrease in sexual pleasure are common symptoms of depression. Depression is more common in patients with cancer than in the general healthy population. It is important that patients discuss their feelings with their doctor. Getting treatment for depression may be helpful in relieving sexual problems.
Cancer treatments may cause physical changes that affect how an individual sees his or her physical appearance. This view can make a man or woman feel sexually unattractive. It is important that patients discuss these feelings and concerns with a health care professional. Patients can learn how to deal effectively with these problems.
The stress of being diagnosed with cancer and undergoing treatment for cancer can make existing problems in relationships even worse. The sexual relationship can also be affected. Patients who do not have a committed relationship may stop dating because they fear being rejected by a potential new partner who learns about their history of cancer. One of the most important factors in adjusting after cancer treatment is the patient's feeling about his or her sexuality before being diagnosed with cancer. If patients had positive feelings about sexuality, they may be more likely to resume sexual activity after treatment for cancer.
Assessment of Sexual Function in People with Cancer
Sexual function is an important factor that adds to quality of life. Patients should discuss their problems and concerns about sexual function with their doctor. Some doctors may not have the appropriate training to discuss sexual problems. Patients should ask for other information resources or for a referral to a health care professional who is comfortable with discussing sexuality issues.
General Factors Affecting Sexual Functioning
When a possible sexual problem is identified, the health care professional will do a detailed interview either with the patient alone or with the patient and his or her partner. The patient may be asked any of the following questions about his or her current and past sexual functioning:
BBC News Health
One in five women with breast cancer who has part of the breast removed, rather than the whole breast, ends up having another operation, a BMJ study suggests.
The reoperation rate increases to one in three for women whose early-stage cancer is difficult to detect.
In England, 58% of women with breast cancer have breast-conserving surgery.
Women should be told of the risk of further operations when choosing surgery, researchers say.
The study, led by researchers from the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine and published in the British Medical Journal, looked at data collected on 55,297 women with breast cancer in England.
They all underwent breast-conserving surgery, rather than a mastectomy, on the NHS between 2005 and 2008. All the women were aged 16 or over.
They then looked at procedures carried out in the three months following the first breast operation.
The researchers took tumour type, age, socio-economic deprivation and other health problems into account.
When combined with radiotherapy, the study says that breast-conserving surgery is as effective as mastectomy, particularly for patients with an obvious, invasive tumour.
‘Emotional distress’
However, because some pre-invasive cancers called ‘carcinoma in situ’ are difficult to detect, because they don’t form a lump, breast conserving-surgery may not remove the cancer completely.
This could result in another operation.
The study says that additional operations put women’s lives on hold while they wait for more surgery. It can delay their return to work, cause emotional distress and result in the need for reconstructive surgery to the breast.
Out of the 55,297 women who underwent breast-conserving surgery, 45,793 (82%) were suffering from isolated invasive cancer, 6,622 (12%) had isolated carcinoma in situ (pre-cancerous disease), and 2,882 (6%) had both types of cancer.
Another operation was more likely among women with pre-cancerous disease (29.5%) compared with those with isolated invasive disease (18%).
Around 40% of women who had a reoperation underwent a mastectomy.
Further results suggest that a repeat operation is less likely in older women and women from more deprived areas.
‘Empowering patients’
Prof Jerome Pereira, study author and consultant breast surgeon at James Paget University Hospitals in Great Yarmouth, said the findings would help women to make decisions about their treatment.
“Patients should feel reassured that clinicians can now advise them more clearly.
“We all have a different attitude to risk but this is empowering patients to make the right decision for themselves.”
Prof Pereira said the study results would help surgeons too.
“This research focuses surgeons and challenges us to try and reduce reoperation rates.
“We need to refine imaging techniques to make this happen – and this opens up more areas for more research.”
‘Increase survival’
Ramsey Cutress, Cancer Research UK breast cancer surgeon at the University of Southampton, said it was standard practice to discuss the possibility of further surgery with patients.
“It’s important for patients to fully understand the pros and cons of surgery. The ultimate aim of these repeat operations after breast-conserving surgery is to reduce the chance that breast cancer will return in the breast, and increase survival from the disease.
“Rates of breast cancer recurrence are also reduced by other treatments such as radiotherapy, hormone therapy and chemotherapy where appropriate.
“There’s an ongoing need to better identify those at high risk of breast cancer recurrence, and to carefully select those who would benefit the most from further surgery.”
Women’s Health – LadyRomp. An extraordinary discovery may someday give the controversial notion of “medical marijuana” a potent new meaning.
Turns out that the recreationally popular cannabis plant contains compounds that could stop and even reverse the growth of various aggressive forms of cancer. The finding, initially reported in 2007, may lead to the development of an effective treatment without toxic side effects.
Since the late 80’s, researchers have investigated the possibility that marijuana may possess anti-tumor properties. It began after a biologist in Madrid noticed that exposing brain cancer cells to tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the chemical responsible for that sensation of being “high,” caused them to die. Follow-up studies conducted at Harvard University confirmed that injections of THC and other compounds known as “cannabinoids” lead to a positive outcome, both slowing down tumor growth by killing cancer cells while leaving healthy cells virtually unscathed.
Now a pair of scientists at California Pacific Medical Center in San Francisco are hoping to take what has been years of promising research a step further. Dr. Pierre Desprez in collaboration with his research partner Sean McAllister found that the compounds halted the spread of cancer cells by disabling ID-1, a gene shown to be a mechanism for the kind of rapid metastasis common in aggressive types of cancer such as lung and brain cancer. After a series of lab tests using a non-psychoactive chemical extract called Cannabidiol to treat malignant human breast cells in mice, the researchers hope to develop a pill that can demonstrate efficacy in human clinical trials.
It took us about 20 years of research to figure this out, but we are very excited,” Desprez, told the Huffington Post. “We want to get started with trials as soon as possible.”
The researchers hope to develop a safe drug that, at the very least, can be integrated into a patient’s treatment program and help to lessen the toxic effects of conventional therapies such as chemotherapy. Another advantage is that as a non-psychoactive chemical, CBD wont produce any mind-altering effects and, in case you’re wondering, it won’t leave the door open for those who want to inhale it.
“We used injections in the animal testing and are also testing pills,” Desprez said. “But you could never get enough Cannabidiol for it to be effective just from smoking.”
An extraordinary discovery may someday give the controversial notion of “medical marijuana” a potent new meaning.
Turns out that the recreationally popular cannabis plant contains compounds that could stop and even reverse the growth of various aggressive forms of cancer. The finding, initially reported in 2007, may lead to the development of an effective treatment without toxic side effects.
Since the late 80’s, researchers have investigated the possibility that marijuana may possess anti-tumor properties. It began after a biologist in Madrid noticed that exposing brain cancer cells to tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the chemical responsible for that sensation of being “high,” caused them to die. Follow-up studies conducted at Harvard University confirmed that injections of THC and other compounds known as “cannabinoids” lead to a positive outcome, both slowing down tumor growth by killing cancer cells while leaving healthy cells virtually unscathed.
Now a pair of scientists at California Pacific Medical Center in San Francisco are hoping to take what has been years of promising research a step further. Dr. Pierre Desprez in collaboration with his research partner Sean McAllister found that the compounds halted the spread of cancer cells by disabling ID-1, a gene shown to be a mechanism for the kind of rapid metastasis common in aggressive types of cancer such as lung and brain cancer. After a series of lab tests using a non-psychoactive chemical extract called Cannabidiol to treat malignant human breast cells in mice, the researchers hope to develop a pill that can demonstrate efficacy in human clinical trials.
It took us about 20 years of research to figure this out, but we are very excited,” Desprez, told the Huffington Post. “We want to get started with trials as soon as possible.”
The researchers hope to develop a safe drug that, at the very least, can be integrated into a patient’s treatment program and help to lessen the toxic effects of conventional therapies such as chemotherapy. Another advantage is that as a non-psychoactive chemical, CBD wont produce any mind-altering effects and, in case you’re wondering, it won’t leave the door open for those who want to inhale it.
“We used injections in the animal testing and are also testing pills,” Desprez said. “But you could never get enough Cannabidiol for it to be effective just from smoking.”