was conceived in classic outlaw fashion. Founded by a successful pot smuggler and radical ’60s activist named Thomas King Forçade, it was intended as a one-time parody of
complete with centerfolds of exotic, voluptuous cannabis plants. But that first issue was a runaway hit, selling more than half a million copies and paving the way for what has become a stoner-American institution. In addition to the requisite grow-scene surveys, pot-price appraisals and joint-rolling tips,
has published writers like Hunter Thompson, William Burroughs, Charles Bukowski, Allen Ginsberg and Truman Capote. It also advocated an end to pot prohibiton at a time when marijuana users were being sentenced to years, even decades, in jail.Forty years later, the magazine has much to celebrate. It has survived the untimely death of its founder, the graying of the counterculture and the dawn of the Internet age, and even some of the laws that created the need for a pro-pot magazine in the first place. It has weathered various government investigations and attacks; founded its annual Cannabis Cup competition in Amsterdam and, more recently, additional Cups in a number of US states, which rank among the biggest marijuana festivals in the world; and published a series of books on everything from cooking with weed to cannabis spirituality. Most importantly, its vision of a day when pot is accepted, even legal, is now proving to be much more than a pipe dream.
We caught up with some of the current and former editors of the self-styled “most dangerous magazine in America” to talk about their role in the long, hard fight for legalization—and their hopes for a cannabis-infused future.
Rick Cusick (associate publisher): High Times was founded by Thomas King Forçade, the number-one East Coast marijuana smuggler in the late ’60s–early ’70s. He was a true revolutionary. He came up with the idea of
High Times in 1974.
Michael Kennedy (general counsel): At the time, I was practicing at an office in a town house that a lawyer and I owned together on East 78th Street. Tom would come in virtually daily and talk about one adventure or another. Tom’s primary activity was flying pot from Jamaica into South Florida, sometimes into Georgia or Alabama. And he was successful at it. It’s why one of the original
High Times logos is an airplane—it’s a mock-up of a DC-3, because that’s what he would fly, loaded to the gills with marijuana. When he founded
High Times, he founded it with that cash—because at the time, you could take cash to the bank and open up a bank account. So Tom started this magazine with dope money.
Rick Cusick: Tom died in 1978. He killed himself, and the memorial was attended by lawyers, pot dealers, rock stars and more lawyers. They wanted to have a special memorial, so they rented the top floor of the World Trade Center so they could be as high as they possibly could. They went to the top of the World Trade Center, and the editors of
High Times and Keith Stroup from NORML approached the family and got a small amount of Tom’s ashes. And they took the ashes from the founder of
High Times and mixed it in with an ounce of marijuana, and they smoked it on the roof of the World Trade Center. And they took a little bit and tossed it off. So I work for a company that smoked its founder. That’s culture.
Michael Kennedy: We were trying to decide how best to subvert the anti-marijuana laws. And one of the ways Tom came up with—and it’s really the seed of genius of
High Times—is teaching people how to grow marijuana. Because if, in fact, you can teach people how to grow, and there’s a First Amendment right to teach, they can start growing under any imaginable circumstances—from your aunt’s sewing basket to a drawer in your college dorm. All you need is a paper towel and a little bit of water, and nature will take care of the rest. If everybody who
wants to grow can learn
how to grow, then there’s no way the government can possibly withstand that subversion.
Steve Hager (former editor in chief): After Tom died, Michael Kennedy stepped in and saved the company. I came in several years later.… You can imagine that the magazine, for years, had just been people doing drugs all day long. People would come in for photographs, and the art director would do lines of coke in the art room, and people would be smoking in every corner. It was nitrous balloons; it was… talk about
fog. It just couldn’t run like that. I wanted it to be a magazine that changed the perspective people had on pot, because at that time, people thought it was the same as cocaine. And I wanted to draw a line and say, “No, no, no—coke is on this line.” It immediately took off and went from teetering on the verge of collapse to selling the best it ever sold.
Michael Kennedy: We started the Cannabis Cup in 1987. Steve Hager went to a half-dozen growers in the Netherlands—we called them “the Dutch Masters”—and said, “We’ll sponsor a Cup here in Amsterdam. Why don’t you bring your very best seeds, your very best buds?” We weren’t too interested in hash or oils back then. Certainly, there were no real edibles or lotions at the time.
Steve Hager: At first, we were just sending little skeleton crews of three people, and the company didn’t want to invest money in it, so I didn’t turn it into a public event until the fifth year. And I had this concept that we were going to base all of our ceremonies around 420, which is something nobody had ever heard of. What had happened was, I’d been sitting outside the office in the stairwell—the only place we could smoke a joint at that time; now we probably can’t smoke at all—and my news editor, Steve Bloom, was carrying a flier he’d picked up at a Grateful Dead show in Oakland. It said, “Come to Mount Tamalpais on April 20th at 4:20.” So I’m looking at this paper, and it says that people are going to meet at 4:20 on April 20 at the top of Mount Tamalpais to smoke pot together. And I think this was an
emanation, a manifestation of the spiritual powers of cannabis. Calling its tribe to its Passover, to its Sermon on the Mount—it’s our baby infant religion, and it’s forming before our eyes.
Michael Kennedy: Today the Cannabis Cup is good branding, quite simply. It allows us to meet the new generation, the young growers. They’re really young and vibrant, God bless ’em. And there’s an entirely new breed of growers who studied agronomy, and studied botany and chemistry, and they are true, scientific twenty-first-century farmers. And they’re developing some of the finest weed imaginable.
Steve Hager: It’s a different event now. It’s a corporate event, and it’s not like what I was trying to do. I was trying to do a real spiritual thing, and when you bought your ticket, you were buying into something that charged your spiritual battery, if you were into that. Most people didn’t ever connect to it on that level—but the ones that did, we
connected. We had a fun time, and we manifested a lot of incredible magic through that.
Michael Kennedy: In the 1990s, we also developed, for a time, a [quarterly] magazine called
Hemp Times. We were quite successful with that in terms of selling the magazine, and we even opened a store called Planet Hemp near the East Village. Our problem was that we were too early, because it was almost impossible to get hemp products then.
Dan Skye (executive editor): We were there trying to push this hemp thing along. We did Hemp Times for four years; we did eighteen issues total. All of us back then thought hemp was really going to open the door and make weed legal, and everything would fall like dominoes. Unfortunately, it didn’t—and what really has done it is medical marijuana.
Michael Kennedy: Tom and I talked a lot before he died about what we imagined the future of marijuana would be, but neither one of us caught on early to the real inroad—that would be the medical properties of marijuana. The research had not been done. So what we knew was that it had a high recreational value, and that we loved it and that many people loved it—but we never imagined anything beyond that. So if today, Tom came back from a desert island and saw the Sanjay Gupta show, he’d say, “Wow… that’s my dream.”
David Bienenstock (feature writer): For about three years, starting in 2010, we had a stand-alone publication about medical marijuana. Legalization is a huge story, but what we’re finding out about the true medical potential of cannabis is a huge, huge story.
Dan Skye: We used to be the bible of marijuana news. You came to High Times to find out about drug war news. And now we have a very successful website. We’ve got a new website director; we got 1 million unique web clicks last month alone. And people want to come to a marijuana festival. The fact that it’s legal for medical use in California, that it’s legal for recreational use in Colorado and Washington—we’ve had these tremendously successful events, the Cannabis Cups. There are Medical Cannabis Cups in places like California and Michigan, and US Cannabis Cups in Colorado and Washington. And I don’t think there’s a trade-off at all. Our magazine’s getting stronger—we’re adding pages. That’s unheard of in this time.
Mary McEvoy (publisher): I was just talking to our printer about the next issue. We got an additional sixteen pages. And after that one, we have our bong special, and we’re thinking about going up in pages for that. So I talked to him, and he said, “You’re the only publisher that I’ve talked to in years that is looking for additional paper to put in the magazine.” We’re not hurting advertisement-wise at this point. The whole media world out there is crying in their booze right now, but we’ve been very lucky. Our readers are very loyal, and our advertisers sure get a response from them.
Danny Danko (senior cultivation editor): Tons of companies are coming in to advertise. A lot of the vapor-pen companies, a lot of the hydroponics companies that sort of shied away from us years ago because they didn’t want that connection to marijuana, have come around because they’re just not afraid of the stigma anymore. That’s one of the things I think High Times has done a good job of—just removing the stigma of the “lazy stoner.” Instead, we try to show that whether it’s in the entertainment business or sports or wherever, we are everywhere. We are doctors and lawyers; we are throughout society and in every part of it. And I think High Times is one of the things that have reinforced the truth rather than the cliché.
Michael Kennedy: The key to High Times’s survival is that I’ve never let High Times break the law. Our clients have broken the law, and our business partners have broken the law, I suppose, and even our advertising people. High Times has survived a lot of grand juries and a lot of inquiries and a lot of attacks from the IRS and what-have-you, but the thing that almost brought us to our knees was in 1989, when the DEA advanced Operation Green Merchant to go after the hydroponics people. All of those advertisers, they were our advertising base. [Federal law enforcement agencies] also kept subpoenaing our subscriber list, and we refused to give it to them. We were threatened with contempt several times. But when they attacked our advertisers and took them out of business—that was the nadir of our existence. And it was really hard to come back.
Around that time, the joke around here was that law enforcement was keeping us in business. Every sheriff in the South had a subscription to High Times. The DEA had I don’t know how many hundreds, the FBI… so there were all these subscriptions.
Chris Simunek (editor in chief): Are they still spying on us? Well, if you’ve read the headlines recently, they are probably spying on all of us. I tell you, when those headlines broke recently and everyone was so shocked that the government was reading our e-mails, I looked at the whole thing and was like, “I always believed that they were doing this.” So I have always gone forward as if the government is reading everything.
Jen Bernstein (managing editor): Are we scared? I think there is always a fear. We went to Detroit and followed every rule in the book. We were at Bert’s Warehouse, which is in downtown Detroit. We were holding a Medical Cannabis Cup, in which we have vendors, and an expo, and seminars, and we provide an open-air smoking area for medical patients in the state of Michigan to come and medicate. The cops came and essentially shut down the smoking area outside. Allowed the expo to continue—they just didn’t want people openly smoking marijuana. And these are legit patients. So, yes, there is a fear, and it’s a fear of us not being able to protect the patients of Michigan. Michigan is not a legal state, so until we have complete legalization, there’s always a risk—because, federally, we are not protected.
Chris Simunek: At the beginning, I was working basically with criminals, trying to get them to do pieces for us. Now that’s gotten easier as the laws have changed. But we’re still dependent on a criminal element to get the job done. We don’t consider them criminals—the laws of America make them criminals. So we work hand in hand. And I would say that’s a pretty big difference between us and Forbes, although I guess Forbes probably works with a lot of criminals, too.
Dan Skye: You’ll see a lot of hypocrisy in the media world. We don’t get access, even though we’re members of the press like anyone else…. Publicists like to get their clients into High Times, but they don’t want their clients to be seen with marijuana, or don’t want them to talk about marijuana. Especially celebrities—we have to deal with that all the time. I’ve interviewed countless celebrities: Bryan Cranston, Alanis Morissette... I did Oliver Stone a few years back. And very seldom will you get somebody to pose with pot. Woody Harrelson wouldn’t even pose with pot! Alanis Morissette was the first really mainstream person who posed in a pot garden. So that’s a real problem—getting people into our ballpark. We like celebrities, but unless they’re on the cover with pot, like Oliver Stone was, we don’t do it.
Chris Simunek: There are some great stars out there that are very pro-pot who have yet to be on the cover. I mean, Rihanna is always Instagramming herself smoking a joint. Zach Galifianakis is pretty cool and forward about it. Those are two I would be interested in…. And I guess you know that Snoop Dogg is still pretty much on top as far as pot-smoking celebrities are concerned. He has managed to maintain his profile for so long and diversify everything he does—products, reality show, pornography, everything from movies to music. His business model, whatever it is, is pretty astounding. He’s a guy that even my dad has heard of, and my dad also knows that he smokes pot.
Bobby Black (senior editor): It used to be, back in the day, it was always rock—psychedelic rock in the ’60s and ’70s—that was the music associated with pot. Then hip-hop came out—well, and reggae, of course, because of the Rasta culture—and they embraced pot in a big way. The thing that’s changed now is that I’m noticing pop stars like Miley Cyrus and Justin Bieber really embracing pot. And it’s not that pop stars never smoked weed before; it’s just that now they’re out about it and don’t really care. It’s become so accepted that the new generation is just like, “So what?”
Dan Skye: Jennifer Aniston! I think she would sell, because we know that she smokes pot—we’ve heard about it for years. We tried; we got no response. And Miley Cyrus is great. We did a poll a few months back: “What celebrity would you most like to smoke with?” And she scored higher than Bill Maher, which we thought was really kind of funny.
Bobby Black: When the magazine started, all throughout the ’70s, sex was an integral part of it. We had beautiful women on the cover. We walk a fine line with it, because we don’t want to be exploiting women. On the other hand, those covers were sexy—and there is nothing wrong with sex. I’ve always stressed this: High Times is about hedonism. But it isn’t about irresponsible, over-the-top hedonism—it’s about enjoying everything life has to offer, and sex is part of that. But the reason we don’t put [former porn star] Jenna Jameson in her bathing suit on the cover anymore is because the sales just weren’t there. Our readers would rather stare at centerfolds of plants—and that’s just the facts we have learned over the years.
David Bienenstock: We’ve never promised a cover to anyone, but if a currently pot-smoking prominent politician is interested in the cover, they should definitely get in touch and talk to us about an exclusive.
Chris Simunek: What I’ve really wanted for High Times is to have more journalism in general. It could be hard-hitting journalism; it could be gonzo journalism. I just want the magazine to have a good read in every single issue—because, if left unchecked, it will by nature fill up with pot pictures and grow stories and stuff like that. It’s almost like I’m the mom at the head of the table saying, “Everybody’s got to eat their vegetables!” I want to maintain the tradition that we’ve always had of having quality journalism in the magazine.
Steve Hager: Have you looked at any of the issues I put out? Because they’re filled with conspiracy stories of deep political events, and incredible forays in counterculture history… and now the magazine just promotes marijuana: “Grow it and smoke it and, now, dab it! And wake up at 7:10 and do some bong hits.” It’s a balls-to-the-wall, marijuana-everythingmagazine. And that’s just making money off marijuana—I don’t think anybody would argue with that statement…. But make money—go, go, go. I’m not anti-capitalist and I’m not anti–big business. That’s not where I’m going to go, but I’m not going to try and stop you. I’m happy with my little magic show here.
Chris Simunek: We do have the High Times haters up there. We just did a cover on dabs. “Dabs” is concentrated hash oil, which is created by a volatile chemical process, similar to the way you would create perfume or rosemary oil. It’s controversial because a lot of kids—I don’t know if they are kids—a lot of idiots who don’t know what they’re doing are renting hotel rooms and cooking this stuff up and blowing themselves up the way meth labs used to blow up. It’s a highly controversial new element to the marijuana world. We are covering it, and we’ve told people how to make dabs safely, but there’s an element that thinks we should be the morality police of the marijuana world. And there’s also this whole crunchy-granola aspect of the marijuana subculture which doesn’t want anything to do with that, and so they’re like: “How dare you? Dabs is like hard drugs! Dabs is this, dabs is that.” Then there’s another element that says we should not tell anybody what to do. So we’re never gonna please everybody at the same time, and I think that’s fine.
Steve Hager: My generation just smoked joints. The next generation went to bong hits. If you grow up smoking bong hits, you can’t smoke joints, because you need that power. And now it’s dabs. Dabbing’s perfectly cool—dab away. But when the sirens are calling, are you going to be able to pull back, or are you going to crash on the rocks? Because if you crash on the rocks… just be advised.
Do I wish my cannabis rituals and other things were still going on? Yeah, but you know what? They are going on. I passed these things down, and people picked up on them, and you see little elements of my rituals all over the cannabis movement. At 4/20, people will be lighting the seven candles of peace. All magic is the same. It doesn’t matter—you can call it religion or whatever you want, but it’s all based on bell, book and candle. These are the elements that are used to manifest prayer and meditation.
David Bienenstock: The biggest change in the ten years I’ve been with High Times—not that long ago in political years—is that, back then, people would say, “Why are you working on pot legalization? That’s never going to happen.” And now people say, “Oh, you’re working on pot legalization? That’s inevitable.” So that’s been the huge change. And I think what’s exciting is that the world is coming around to where High Times was at its founding—long before I was involved, or even alive.
Chris Simunek: We used to change people’s identities a lot. Back then, when you’re talking to a guy breaking a federal law which is going to land him in jail for quite a few years, I didn’t have any journalistic qualms about saying he came from Alabama when he came from Ohio, you know? I remember being blindfolded in the back of a car and being brought to some growroom in the basement of a guy’s house… that’s how paranoid he was. Now I get people e-mailing me with their full name and address saying, “I want you to come to my 5,000-square-foot house in Colorado—and bring your photographers.” I just think the access has changed, and people aren’t afraid anymore.
Jen Bernstein: When I took my job at High Times, I spoke with my parents and explained to them what I was joining. My dad knew what it was and my mom didn’t. But they feel like if it’s meant to be, it will be. And now my dad came with me to the Cannabis Cup and was a worker and got a High Times hoodie. My dad is in Charlotte, North Carolina, and he wears this hoodie that says “Cannabis Cup,” and people stop him and are like, “Oh, did you go to the Cup?” And he’s like, “Yeah, I did. I worked there.” So I think they’re proud of me now, and all their friends know what it is even though they may not smoke pot themselves…. How would your parents take it?
Danny Danko: When I started off in the cultivation department, I had to ride in the trunk of a car to go and see some of these growrooms. People were so scared to show me regular-size—well, what I would consider fairly average-size—grows. Now you go and see thesemassive operations in California, Colorado—all over, really—and I never thought I would see the day that people would be walking me on tours of huge, indoor pot-growing facilities that are perfectly legal under state law. It is kind of mind-blowing… but once the dominoes start to fall, they fall so fast it’s hard to keep up.
Elise McDonough (West Coast design and production director): After the medical marijuana laws started to pass, especially on the West Coast, more and more people got into making edibles and distributing them through collectives and dispensaries. We’re in an era where people go way beyond the pot brownie. Now you see cannabis in savory sauces, drink mixes, candy bars. You’re just getting better and better edibles, and the thing that’s advancing the industry is lab testing. Before, you couldn’t tell how much THC you’d get in a dose—but now you can test and know exactly how much you’re going to ingest. It’s especially helpful for people who are insomniacs or chronic-pain patients. The difference between smoking and eating pot is that you have a body effect that lasts longer, so if you have back pain, you can get relief for six to eight hours.
The first story in High Times about edibles was called “Eat It,” in 1978. That was a story written by a guy who worked as a sailor and traveled around the world and tried edible marijuana in Turkey and Greece. He had a hash candy called majoun, which is hash sautéed in butter with mixed dates and nuts and spices rolled into a ball. It’s like a baklava without filo dough.
We also had Chef Ra’s “Psychedelic Kitchen” column, which started in the ’80s. Chef Ra, sadly, passed away several years ago, but we’ve continued the recipe column with different contributing chefs along the way. We do recipes online, and there’s also a recipe in the magazine every month.
Bobby Black: I wouldn’t say I consider us “the most dangerous magazine in America.” The most notorious, maybe, but not dangerous. We’ve represented an outlaw and counterculture ethos for so long that, like you say, it’s becoming mainstream now. But what I would also like to say is that we haven’t come to the mainstream; the mainstream has come to us. The same thing is true with civil rights, the revolution in the ’60s, the sexual revolution.
Danny Danko: I think that with the Internet, the distinction between mainstream culture and the counterculture is fading. I don’t think there is any one counterculture. That’s always sort of been associated with the hippie movement, which is a part of our culture—but it’s not all of our culture. We reach out to all. Marijuana users are everybody, and we try to reach out to all of them.
Rick Cusick: Every year, I go to the Boston Freedom Rally and give a speech. We’re sponsors of the rally. It’s been going on for twenty-four years, and there were over 30,000 people there last year. I was there in 2007 with Keith Stroup from NORML. It was kind of rainy, and Keith said, “You want to smoke a joint?” And I said sure. Then this kid came up to us. We thought he wanted a hit, but he was an undercover cop. He had no idea who we were. So he took us to a tent where they arraigned people. They said, “Step up—what’s your name?” I said, “Rick Cusick.” They said, “Where do you live?” Told ’em. “What’s your Social Security number?” Told ’em. “What do you do?” I said—this was at the time—“I’m the co-editor ofHigh Times magazine.” And the cop looked up and said, “You’re kidding.” I said, “Wait, it gets better!” I slapped Keith on the back and said, “This is Keith Stroup, the founder of NORML and my attorney. And everything we say is on the record.” And they said, “You’re going to write about this?” And I said, “Oh, yeah!”
So we got arrested for a joint, and they arrested sixty people that day. Every year, they arrested a quota of about sixty kids under 25—except this year they got a couple of old guys, and it was early in the game. So we went in there, and of the sixty they arrested, fifty-eight settled and paid their fine. We said no. And so what happened was, we got a NORML lawyer, and Dr. Lester Grinspoon of Harvard University—Keith’s friend; I didn’t known him at that point—got involved in what we were doing and started a defense fund that contributed a very good amount of money for us to travel back and forth. And then he got Dr. Charles Nesson of the Harvard Law School, who worked on the Pentagon Papers case, to be our defense counsel.
After that happened, we had the dream team of American jurisprudence going after a third of a joint. And it took two and a half years. First, the jury found us guilty, because we were. Then we appealed it. The appeal went all the way to the Appeals Court, which was an incredible experience—very high-flown legal stuff. Everybody came in; it was covered in the papers a bit. Then the Appeals Court upheld the lower court, so we went to the Supreme Court of Massachusetts, and they refused to hear the case and sent it back down for sentencing. But in the meantime, Massachusetts had decriminalized marijuana—so Keith and I were the last two people sentenced under the old law. And they tried to throw the book at us. The prosecutor said, “I want a six-month suspended sentence, two years’ probation, a $500 fine and fifty hours of community service cleaning up the Boston Common.” And I swear to God, he also asked the judge to prohibit us from entering the Boston Common for two years—“which should keep them from making speeches.” That’s an exact quote. And we looked at each other and said, “Did this guy go to law school?” That’s the First Amendment; it’s the Boston Common! They bled there for the First Amendment, and you’re asking that we be excluded from the fucking Boston Common? And the judge said, “Normally, this is where I go back to my chamber and think about this, but I don’t have to think about this. Everybody stand up. You’re sentenced to jail for one day—equal to the amount of time you were in the custody of the Boston police.” And then it was all over.
Michael Kennedy: Things have changed dramatically since we started the magazine. But I, personally, can never feel a sense of vindication, primarily because I am so steeped in the laws inflicted on people. I know that Tom would be buoyant and feel vindicated immediately. But then he would say, “Our job isn’t finished until we get every person who’s in prison under any form of marijuana conviction out.” It’s one of the reasons that High Times hired me. I’m their lawyer, and now I ended up being one of the principals. I’m still basically their lawyer. I’ve done marijuana cases for as long as I can remember, and there are still people who have done twenty years in prison or have life sentences for no violence—just pot. They got life in prison with no possibility of parole. Now that’s very hard to believe.
David Bienenstock: I feel great about the changes in the pot world, provided we learn the right lessons. You look at the mainstream and the corporate press, there’s this idea and this rash of stories that now that Wall Street is getting involved, marijuana is legitimate. The idea that the marijuana industry needs to take its ethics lessons from Wall Street is ridiculous. And second of all, it’s really offensive to people who have not just spent their time and energy making this happen, but in many, many cases risked their freedom quite literally. So to see the issue hitting the mainstream is fantastic, but I think we need to learn the right lesson—which is that the counterculture was right about this. Not that Wall Street and big business are going to legitimize it. I think that’s exactly the wrong lesson.
 Sexuality is a complex characteristic that involves the physical, psychological, interpersonal, and behavioral aspects of a person. Recognizing that "normal" sexual functioning covers a wide range is important. Ultimately, sexuality is defined by each patient and his/her partner according to sex, age, personal attitudes, and religious and cultural values.
Many types of cancer and cancer therapies can cause sexual dysfunction. Research shows that approximately 50% of women who have been treated for breast and gynecologic cancers experience long-term sexual dysfunction. Nearly 70% of men who have been treated for prostate cancer experience long-term sexual dysfunction.
An individual's sexual response can be affected in many ways. The causes of sexual dysfunction are often both physical and psychological. The most common sexual problems for people who have cancer are loss of desire for sexual activity in both men and women, problems achieving and maintaining an erection in men, and pain with intercourse in women. Men may also experience inability to ejaculate, ejaculation going backward into the bladder, or the inability to reach orgasm. Women may experience a change in genital sensations due to pain, loss of sensation and numbness, or decreased ability to reach orgasm. Most often, both men and women are still able to reach orgasm, however, it may be delayed due to medications and/or anxiety.
Unlike many other physical side effects of cancer treatment, sexual problems may not resolve within the first year or two of disease-free survival and can interfere with the return to a normal life. Patients recovering from cancer should discuss their concerns about sexual problems with a health care professional.
Factors Affecting Sexual Function in People With Cancer
Both physical and psychological factors contribute to the development of sexual dysfunction. Physical factors include loss of function due to the effects of cancer therapies, fatigue, and pain. Surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy may have a direct physical impact on sexual function. Other factors that may contribute to sexual dysfunction include pain medications, depression, feelings of guilt from misbeliefs about the origin of the cancer, changes in body image after surgery, and stresses due to personal relationships. Getting older is often associated with a decrease in sexual desire and performance, however, sex may be important to the older person's quality of life and the loss of sexual function can be distressing.
Surgery-Related Factors
Surgery can directly affect sexual function. Factors that help predict a patient's sexual function after surgery include age, sexual and bladder function before surgery, tumor location and size, and how much tissue was removed during surgery. Surgeries that affect sexual function include breast cancer, colorectal cancer, prostate cancer, and other pelvic tumors.
Breast Cancer
Sexual function after breast cancer surgery has been the subject of much research. Surgery to save or reconstruct the breast appears to have little effect on sexual function compared with surgery to remove the whole breast. Women who have surgery to save the breast are more likely to continue to enjoy breast caressing, but there is no difference in areas such as how often women have sex, the ease of reaching orgasm, or overall sexual satisfaction.
Colorectal Cancer
Sexual and bladder dysfunctions are common complications of surgery for rectal cancer. The main cause of problems with erection, ejaculation, and orgasm is injury to nerves in the pelvic cavity. Nerves can be damaged when their blood supply is disrupted or when the nerves are cut.
Prostate Cancer
Newer nerve-sparing techniques for radical prostatectomy are being debated as a more successful approach for preserving erectile function than radiation therapy for prostate cancer. Long-term follow-up is needed to compare the effects of surgery with the effects of radiation therapy. Recovery of erectile function usually occurs within a year after having a radical prostatectomy. The effects of radiation therapy on erectile function are very slow and gradual occurring for two or three years after treatment. The cause of loss of erectile function differs between surgery and radiation therapy. Radical prostatectomy damages nerves that make blood vessels open wider to allow more blood into the penis. Eventually the tissue does not get enough oxygen, cells die, and scar tissue forms that interferes with erectile function. Radiation therapy appears to damage the arteries that bring blood to the penis.
Other Pelvic Tumors
Men who have surgery to remove the bladder, colon, and/or rectum may improve recovery of erectile function if nerve-sparing surgical techniques are used. The sexual side effects of radiation therapy for pelvic tumors are similar to those after prostate cancer treatment. Women who have surgery to remove the uterus, ovaries, bladder, or other organs in the abdomen or pelvis may experience pain and loss of sexual function depending on the amount of tissue/organ removed. With counseling and other medical treatments, these patients may regain normal sensation in the vagina and genital areas and be able to have pain-free intercourse and reach orgasm.
Chemotherapy-Related Factors
Chemotherapy is associated with a loss of desire and decreased frequency of intercourse for both men and women. The common side effects of chemotherapy such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, mucositis, weight loss or gain, and loss of hair can affect an individual's sexual self-image and make him or her feel unattractive.
For women, chemotherapy may cause vaginal dryness, pain with intercourse, and decreased ability to reach orgasm. In older women, chemotherapy may increase the risk of ovarian cancer. Chemotherapy may also cause a sudden loss of estrogen production from the ovaries. The loss of estrogen can cause shrinking, thinning, and loss of elasticity of the vagina, vaginal dryness, hot flashes, urinary tract infections, mood swings, fatigue, and irritability. Young women who have breast cancer and have had surgeries such as removal of one or both ovaries, may experience symptoms related to loss of estrogen. These women experience high rates of sexual problems since there is a concern that estrogen replacement therapy, which may decrease these symptoms, could cause the breast cancer to return. For women with other types of cancer, however, estrogen replacement therapy can usually resolve many sexual problems. Also, women who have graft-versus-host disease (a reaction of donated bone marrow or peripheral stem cells against a person's tissue) following bone marrow transplantation may develop scar tissue and narrowing of the vagina that can interfere with intercourse.
For men, sexual problems such as loss of desire and erectile dysfunction are more common after a bone marrow transplant because of graft-versus-host disease or nerve damage. Occasionally chemotherapy may interfere with testosterone production in the testicles. Testosterone replacement may be necessary to regain sexual function.
Radiation Therapy-Related Factors
Like chemotherapy, radiation therapy can cause side effects such as fatigue, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, and other symptoms that can decrease feelings of sexuality. In women, radiation therapy to the pelvis can cause changes in the lining of the vagina. These changes eventually cause a narrowing of the vagina and formation of scar tissue that results in pain with intercourse, infertility and other long term sexual problems. Women should discuss concerns about these side effects with their doctor and ask about the use of a vaginal dilator.
For men, radiation therapy can cause problems with getting and keeping an erection. The exact cause of sexual problems after radiation therapy is unknown. Possible causes are nerve injury, a blockage of blood supply to the penis, or decreased levels of testosterone. Sexual changes occur very slowly over a period of six months to one year after radiation therapy. Men who had problems with erectile dysfunction before getting cancer have a greater risk of developing sexual problems after cancer diagnosis and treatment. Other risk factors that can contribute to a greater risk of sexual problems in men are cigarette smoking, history of heart disease, high blood pressure, and diabetes.
Hormone Therapy-Related Factors
Hormone therapy for prostate cancer can decrease normal hormone levels and cause a decrease in sexual desire, erectile dysfunction, and problems reaching orgasm. Younger men do not always experience the same degree of sexual dysfunction. Some treatment centers are experimenting with delayed or intermittent hormone therapy to prevent sexual problems. It is not yet known if these modified treatments affect the long-term survival of younger men.
The effects of tamoxifen on the sexuality and mood of women who have breast cancer are not clearly understood.
Psychological Factors
Patients recovering from cancer often have anxiety or guilt that previous sexual activities may have caused their cancer. Some patients believe that sexual activity may cause the cancer to return or pass the cancer to their partner. Discussing their feelings and concerns with a health care professional is important for patients. Misbeliefs can be corrected and patients can be reassured that cancer is not passed on through sexual contact.
Loss of sexual desire and a decrease in sexual pleasure are common symptoms of depression. Depression is more common in patients with cancer than in the general healthy population. It is important that patients discuss their feelings with their doctor. Getting treatment for depression may be helpful in relieving sexual problems.
Cancer treatments may cause physical changes that affect how an individual sees his or her physical appearance. This view can make a man or woman feel sexually unattractive. It is important that patients discuss these feelings and concerns with a health care professional. Patients can learn how to deal effectively with these problems.
The stress of being diagnosed with cancer and undergoing treatment for cancer can make existing problems in relationships even worse. The sexual relationship can also be affected. Patients who do not have a committed relationship may stop dating because they fear being rejected by a potential new partner who learns about their history of cancer. One of the most important factors in adjusting after cancer treatment is the patient's feeling about his or her sexuality before being diagnosed with cancer. If patients had positive feelings about sexuality, they may be more likely to resume sexual activity after treatment for cancer.
Assessment of Sexual Function in People with Cancer
Sexual function is an important factor that adds to quality of life. Patients should discuss their problems and concerns about sexual function with their doctor. Some doctors may not have the appropriate training to discuss sexual problems. Patients should ask for other information resources or for a referral to a health care professional who is comfortable with discussing sexuality issues.
General Factors Affecting Sexual Functioning
When a possible sexual problem is identified, the health care professional will do a detailed interview either with the patient alone or with the patient and his or her partner. The patient may be asked any of the following questions about his or her current and past sexual functioning:
Sexuality is a complex characteristic that involves the physical, psychological, interpersonal, and behavioral aspects of a person. Recognizing that "normal" sexual functioning covers a wide range is important. Ultimately, sexuality is defined by each patient and his/her partner according to sex, age, personal attitudes, and religious and cultural values.
Many types of cancer and cancer therapies can cause sexual dysfunction. Research shows that approximately 50% of women who have been treated for breast and gynecologic cancers experience long-term sexual dysfunction. Nearly 70% of men who have been treated for prostate cancer experience long-term sexual dysfunction.
An individual's sexual response can be affected in many ways. The causes of sexual dysfunction are often both physical and psychological. The most common sexual problems for people who have cancer are loss of desire for sexual activity in both men and women, problems achieving and maintaining an erection in men, and pain with intercourse in women. Men may also experience inability to ejaculate, ejaculation going backward into the bladder, or the inability to reach orgasm. Women may experience a change in genital sensations due to pain, loss of sensation and numbness, or decreased ability to reach orgasm. Most often, both men and women are still able to reach orgasm, however, it may be delayed due to medications and/or anxiety.
Unlike many other physical side effects of cancer treatment, sexual problems may not resolve within the first year or two of disease-free survival and can interfere with the return to a normal life. Patients recovering from cancer should discuss their concerns about sexual problems with a health care professional.
Factors Affecting Sexual Function in People With Cancer
Both physical and psychological factors contribute to the development of sexual dysfunction. Physical factors include loss of function due to the effects of cancer therapies, fatigue, and pain. Surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy may have a direct physical impact on sexual function. Other factors that may contribute to sexual dysfunction include pain medications, depression, feelings of guilt from misbeliefs about the origin of the cancer, changes in body image after surgery, and stresses due to personal relationships. Getting older is often associated with a decrease in sexual desire and performance, however, sex may be important to the older person's quality of life and the loss of sexual function can be distressing.
Surgery-Related Factors
Surgery can directly affect sexual function. Factors that help predict a patient's sexual function after surgery include age, sexual and bladder function before surgery, tumor location and size, and how much tissue was removed during surgery. Surgeries that affect sexual function include breast cancer, colorectal cancer, prostate cancer, and other pelvic tumors.
Breast Cancer
Sexual function after breast cancer surgery has been the subject of much research. Surgery to save or reconstruct the breast appears to have little effect on sexual function compared with surgery to remove the whole breast. Women who have surgery to save the breast are more likely to continue to enjoy breast caressing, but there is no difference in areas such as how often women have sex, the ease of reaching orgasm, or overall sexual satisfaction.
Colorectal Cancer
Sexual and bladder dysfunctions are common complications of surgery for rectal cancer. The main cause of problems with erection, ejaculation, and orgasm is injury to nerves in the pelvic cavity. Nerves can be damaged when their blood supply is disrupted or when the nerves are cut.
Prostate Cancer
Newer nerve-sparing techniques for radical prostatectomy are being debated as a more successful approach for preserving erectile function than radiation therapy for prostate cancer. Long-term follow-up is needed to compare the effects of surgery with the effects of radiation therapy. Recovery of erectile function usually occurs within a year after having a radical prostatectomy. The effects of radiation therapy on erectile function are very slow and gradual occurring for two or three years after treatment. The cause of loss of erectile function differs between surgery and radiation therapy. Radical prostatectomy damages nerves that make blood vessels open wider to allow more blood into the penis. Eventually the tissue does not get enough oxygen, cells die, and scar tissue forms that interferes with erectile function. Radiation therapy appears to damage the arteries that bring blood to the penis.
Other Pelvic Tumors
Men who have surgery to remove the bladder, colon, and/or rectum may improve recovery of erectile function if nerve-sparing surgical techniques are used. The sexual side effects of radiation therapy for pelvic tumors are similar to those after prostate cancer treatment. Women who have surgery to remove the uterus, ovaries, bladder, or other organs in the abdomen or pelvis may experience pain and loss of sexual function depending on the amount of tissue/organ removed. With counseling and other medical treatments, these patients may regain normal sensation in the vagina and genital areas and be able to have pain-free intercourse and reach orgasm.
Chemotherapy-Related Factors
Chemotherapy is associated with a loss of desire and decreased frequency of intercourse for both men and women. The common side effects of chemotherapy such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, mucositis, weight loss or gain, and loss of hair can affect an individual's sexual self-image and make him or her feel unattractive.
For women, chemotherapy may cause vaginal dryness, pain with intercourse, and decreased ability to reach orgasm. In older women, chemotherapy may increase the risk of ovarian cancer. Chemotherapy may also cause a sudden loss of estrogen production from the ovaries. The loss of estrogen can cause shrinking, thinning, and loss of elasticity of the vagina, vaginal dryness, hot flashes, urinary tract infections, mood swings, fatigue, and irritability. Young women who have breast cancer and have had surgeries such as removal of one or both ovaries, may experience symptoms related to loss of estrogen. These women experience high rates of sexual problems since there is a concern that estrogen replacement therapy, which may decrease these symptoms, could cause the breast cancer to return. For women with other types of cancer, however, estrogen replacement therapy can usually resolve many sexual problems. Also, women who have graft-versus-host disease (a reaction of donated bone marrow or peripheral stem cells against a person's tissue) following bone marrow transplantation may develop scar tissue and narrowing of the vagina that can interfere with intercourse.
For men, sexual problems such as loss of desire and erectile dysfunction are more common after a bone marrow transplant because of graft-versus-host disease or nerve damage. Occasionally chemotherapy may interfere with testosterone production in the testicles. Testosterone replacement may be necessary to regain sexual function.
Radiation Therapy-Related Factors
Like chemotherapy, radiation therapy can cause side effects such as fatigue, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, and other symptoms that can decrease feelings of sexuality. In women, radiation therapy to the pelvis can cause changes in the lining of the vagina. These changes eventually cause a narrowing of the vagina and formation of scar tissue that results in pain with intercourse, infertility and other long term sexual problems. Women should discuss concerns about these side effects with their doctor and ask about the use of a vaginal dilator.
For men, radiation therapy can cause problems with getting and keeping an erection. The exact cause of sexual problems after radiation therapy is unknown. Possible causes are nerve injury, a blockage of blood supply to the penis, or decreased levels of testosterone. Sexual changes occur very slowly over a period of six months to one year after radiation therapy. Men who had problems with erectile dysfunction before getting cancer have a greater risk of developing sexual problems after cancer diagnosis and treatment. Other risk factors that can contribute to a greater risk of sexual problems in men are cigarette smoking, history of heart disease, high blood pressure, and diabetes.
Hormone Therapy-Related Factors
Hormone therapy for prostate cancer can decrease normal hormone levels and cause a decrease in sexual desire, erectile dysfunction, and problems reaching orgasm. Younger men do not always experience the same degree of sexual dysfunction. Some treatment centers are experimenting with delayed or intermittent hormone therapy to prevent sexual problems. It is not yet known if these modified treatments affect the long-term survival of younger men.
The effects of tamoxifen on the sexuality and mood of women who have breast cancer are not clearly understood.
Psychological Factors
Patients recovering from cancer often have anxiety or guilt that previous sexual activities may have caused their cancer. Some patients believe that sexual activity may cause the cancer to return or pass the cancer to their partner. Discussing their feelings and concerns with a health care professional is important for patients. Misbeliefs can be corrected and patients can be reassured that cancer is not passed on through sexual contact.
Loss of sexual desire and a decrease in sexual pleasure are common symptoms of depression. Depression is more common in patients with cancer than in the general healthy population. It is important that patients discuss their feelings with their doctor. Getting treatment for depression may be helpful in relieving sexual problems.
Cancer treatments may cause physical changes that affect how an individual sees his or her physical appearance. This view can make a man or woman feel sexually unattractive. It is important that patients discuss these feelings and concerns with a health care professional. Patients can learn how to deal effectively with these problems.
The stress of being diagnosed with cancer and undergoing treatment for cancer can make existing problems in relationships even worse. The sexual relationship can also be affected. Patients who do not have a committed relationship may stop dating because they fear being rejected by a potential new partner who learns about their history of cancer. One of the most important factors in adjusting after cancer treatment is the patient's feeling about his or her sexuality before being diagnosed with cancer. If patients had positive feelings about sexuality, they may be more likely to resume sexual activity after treatment for cancer.
Assessment of Sexual Function in People with Cancer
Sexual function is an important factor that adds to quality of life. Patients should discuss their problems and concerns about sexual function with their doctor. Some doctors may not have the appropriate training to discuss sexual problems. Patients should ask for other information resources or for a referral to a health care professional who is comfortable with discussing sexuality issues.
General Factors Affecting Sexual Functioning
When a possible sexual problem is identified, the health care professional will do a detailed interview either with the patient alone or with the patient and his or her partner. The patient may be asked any of the following questions about his or her current and past sexual functioning:

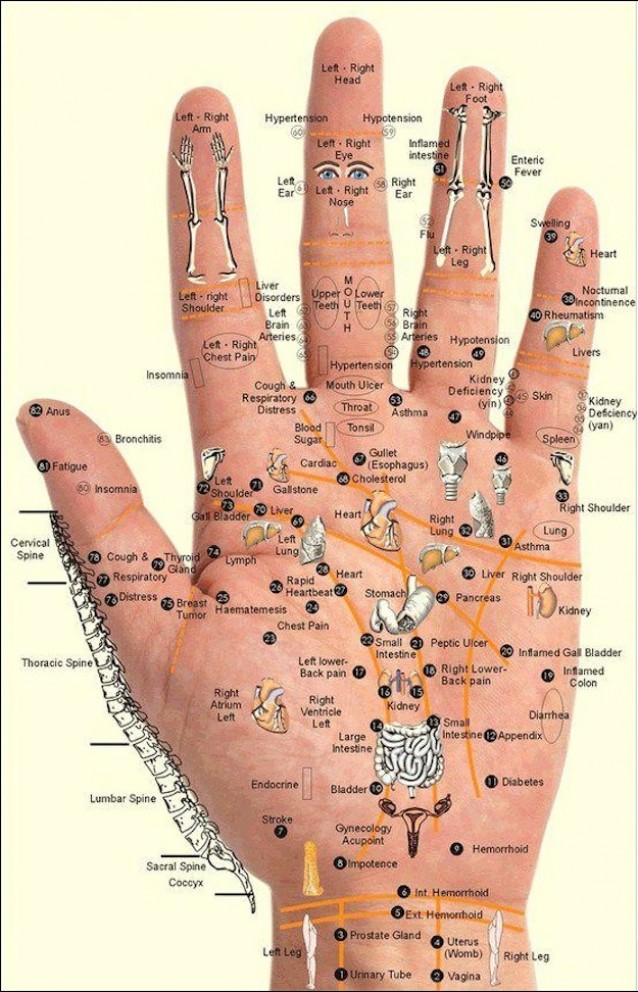 This Chart and Techniques for Hand Reflexology and Massage of Meridian points shows us where and how to use our own personal power and take charge of our health.
This Chart and Techniques for Hand Reflexology and Massage of Meridian points shows us where and how to use our own personal power and take charge of our health.